Internal Control Systems And Internal Audit Function
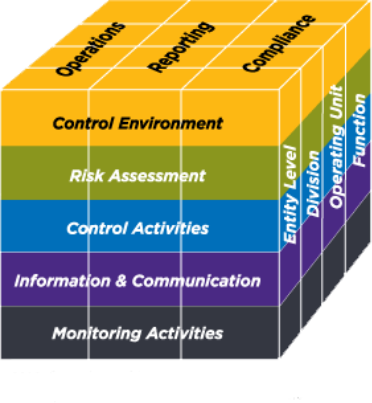
Internal Control System
The report should describe the roles of the board, audit committee, and senior management in the internal controls of the company, including the following:
- Financial accounting and reporting controls;
- Nonfinancial accounting and reporting controls;
- Operational controls, including sustainability and stakeholder risks (worker, consumer, community health and safety);
- Compliance controls, including ethics and compliance: code of ethics, whistleblower systems, anticorruption measures.
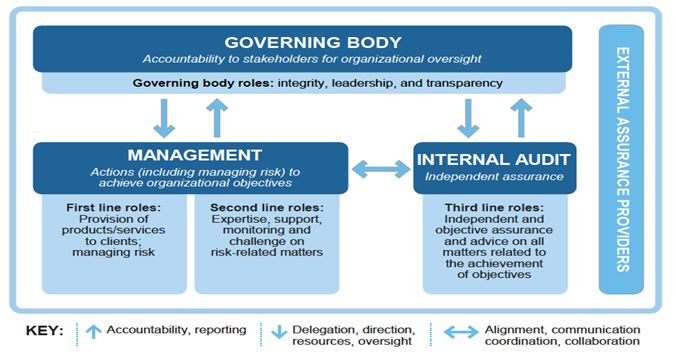
Internal Audit Function
The report should describe how the board is carrying out its responsibility to ensure the financial integrity and the integrity of its operations, including:
- Auditor’s reporting to the audit committee, and relationship with management;
- Main activities, challenges, and findings of the internal audit;
- How the internal audit function is carried out, including by an external firm;
- Assessment of ESG policies and practices and IT and security systems;
- Corrective action on control deficiencies, including those highlighted in the external auditor’s letter
The internal audit function should:
- be independent, objective, risk-based, and empowered with an unlimited scope of activities
- be subject to periodic quality assessment by a third party
- report directly to the audit committee and administratively to management
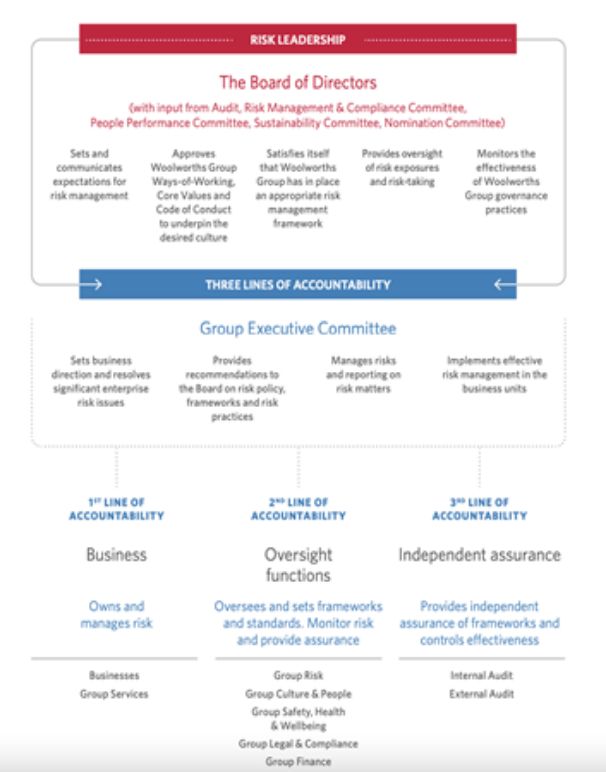
audit committee
The report should describe the role and deliberations of the audit committee, including oversight of the following:
- accurate financial statements
- internal and external audit process,
- related-party transactions
- quality of sustainability information
- if there is no risk committee, risk oversight and management.
Sometimes more justification may be necessary in situations where independence seems compromised.
External Auditor
The report should describe:
- Tenure, qualifications, and independence of the external auditor, and the effect of any long association on independence;
- Non-audit work by the external auditor and its impact, if any, on the independence of the audit, plus a breakdown of audit and non-audit fees
- Periodic assessment of the quality of the external audit;
- Corrective actions taken on issues raised in the external auditor management letter;
- Any Audit Quality Indicators used in monitoring the effectiveness of the External Auditor.
- Role of audit committee overseeing the external auditor and in agreeing to the audit plan.