Corporate disclosure and transparency bring a number of benefits– both internal and external, especially when it provides a comprehensive picture of the company and how it creates value on all capitals, not just financial and for all key stakeholders, not just investors.
Rigorous ESG reporting helps to match responsible investors with sustainable companies. Transparent, accountable disclosure can help increase trust with many different stakeholders, including customers and communities.
Why do investors value ESG disclosure?
High-quality ESG disclosure can help companies access capital provided by the growing number of investors seeking positive societal and environmental impact.
While all stakeholders are demanding more transparency, investors are seeking and expecting more and more ESG information. ESG issues are of growing interest to institutional investors because of their significance in investment decisions and future portfolio performance. This interest has created major changes in the pattern of investments around the world.
Some companies invest in disclosure to boost their reputation and improve understanding of their value creation approach. Transparency is generally seen as a sign that a company operates a reputable, well-managed business.
Enhanced disclosure can clarify the links between corporate strategy and ESG risks. To continue to thrive, companies need to build their resilience, enhance their license to operate, and commit to long term, sustainable value creation that embraces the wider demands of society. This involves a shift in reporting, as well as management focus.
A company can internally benefit from better ESG performance in many ways:
When a company improves disclosure and transparency, it enhances internal data quality, especially for decision-making. It also identifies gaps in ESG practices and improves risk management. Moreover, better disclosure and transparency can help raise awareness, educate board directors about emerging material risks and opportunities, and improve collaboration with the management.
More than half of all stock exchanges worldwide now have guidance on ESG disclosure. Many countries are adopting stewardship codes to recognize investor fiduciary responsibility and increase institutional investor accountability for ESG factors. These situations are leading to not only changes in investor behavior but changes in transparency and disclosure.
The Interactive Tool provides practical guidance on the different topics that companies should address in their communication with investors and other stakeholders, including in their annual reports.
Outlining the main content elements of a model annual report, structured around a company’s strategy, governance, and performance.
Strategy is the formulation of long-term goals and objectives of a company, and the actions taken and resource needed to achieve these goals, based on the internal and external environments in which the organization competes.
Corporate governance is a set of structures and processes for the direction and control of companies. It establishes the rights and responsibilities of – and the relationship among – key actors in the company, including management, shareholders and creditors, and stakeholders.
Performance is a detailed account of how the company performed against its strategic goals and objectives. It includes an overall assessment of performance by management and the presentation of detailed financial and sustainability results.
Reporting on strategy helps investors and other stakeholders understand what the organization does and how it does it, providing important insight regarding an organization’s future. It answers the question: What does the organization want to achieve and how does it plan to achieve it?
Complete, transparent strategy disclosure includes:



The strategy overview describes what the company plans to do, how it conducts its activities and the expected results and impacts. It includes an overview by management with an explanation of progress and setbacks in the implementation of the strategy, and any change of plans.
learn moreThe business model describes what the company does and how it does it. It includes the company’s main products and services, its customers, and where it fits in the value chain for the industry. It also describes the business processes that are most important to the creation of long-term value.
learn moreThe external environment is the context in which the company operates, including the relationships, resources and input necessary for the business to succeed. It includes the company’s markets, legal environment, and internal cost drivers.
learn moreReporting on stakeholder engagement provides an understanding of the company’s key stakeholders and their concerns, and how their interest and preferences are considered in the strategy and its implementation.
learn moreStrategic objectives provide a sense where the company is heading, and how it plans to get there. It includes plans and initiatives as well as financing and other resources needed for specific investments. It also includes KPIs to measure progress towards key objectives.
learn moreThe report should describe the process of identifying and managing the company’s internal and external risks, to ensure that it achieve its strategy, remain profitable and create value for all stakeholders.
learn moreReporting on material sustainability issues provides a more comprehensive view of value creation, considering the interests of various stakeholders, including investors, workers, customers, communities, and the environment. It should include the process for identifying and managing material sustainability issues
learn moreIt is critical for investors and other stakeholders to understand how companies are governed and managed:
The report should demonstrate the company’s leadership and culture and its commitment to sound corporate governance and the governance and management of ethical, environmental and social issues.
learn moreThe report should establish that the board is qualified and adequately structured to oversee the strategy, management, and performance of the company. It should also describe the main focus of the board and its committees during the year.
learn moreReporting on the internal control systems of the company, including internal audit, risk management (including E&S), and compliance provides insight into the control environment and whether it can ensure sound stewardship of the company.
learn moreThe report should describe role of the board in overseeing stakeholder engagement and ensuring that proper mechanisms are in place, including stakeholder mapping, engagement policy and grievance mechanisms.
learn moreThe report should describe governance mechanisms to ensure that the company’s financial and nonfinancial disclosures are a relevant, faithful, and timely representation of material events to shareholders and other stakeholders.
learn morePerformance information is an opportunity for management to be accountable to investors and stakeholders on how the company was able to deliver on its strategic objectives and maximize its contribution to society.
It also includes the presentation of financial sustainability results and position of the company at the end of the period, how these relate to previous year, whether they depart from forecasted financial results or long-term trends.
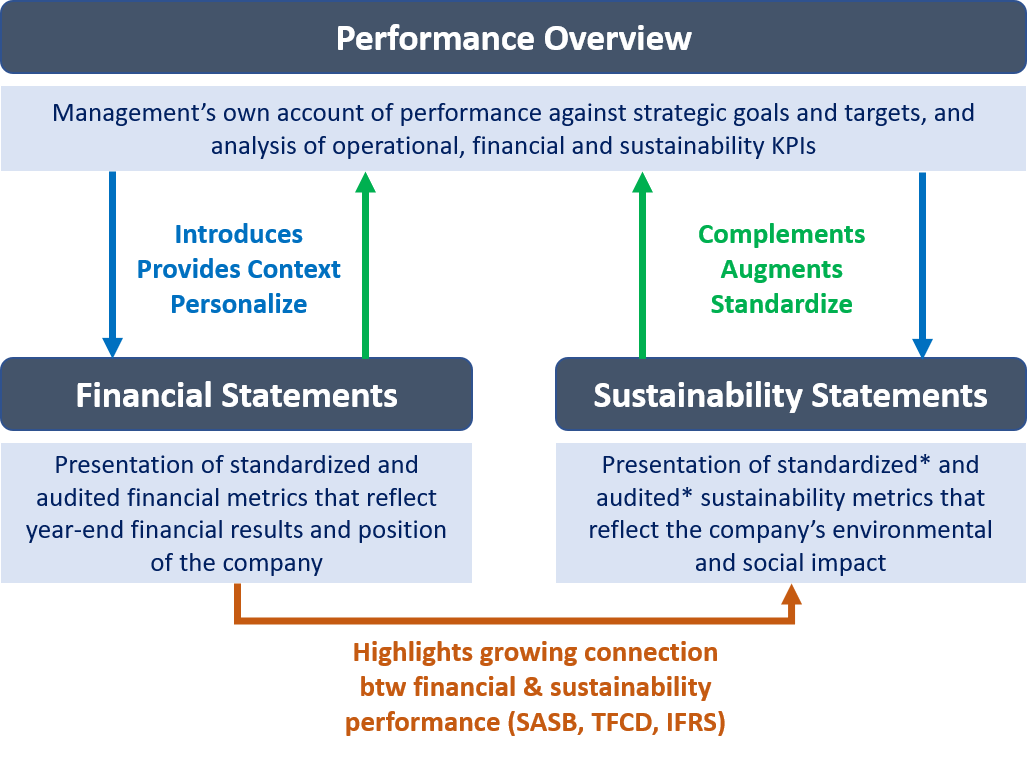
The performance overview is management’s own account of performance against strategic goals and targets, and analysis of operational, financial and sustainability KPIs. It provides an analysis of financial operational and financial performance, including material changes or trends, liquidity, capital requirements and investments. It also looks at intangibles and non-financial performance, including material sustainability issues and the links between financial and non-financial performance.
learn moreFinancial statements present standardized and audited financial metrics that reflect the financial results and position of the company. This includes the balance sheet and statements of income, cash flows and change in stockholders' equity. It also includes notes to financial statements and segment reporting.
learn moreSustainability statements present standardized and audited sustainability metrics that reflect the company’s environmental and social impact, and ultimately account for its contribution to sustainable development (SDGs). They are derived from the most reported ESG metrics but adapted to the operating context of the company.
learn morePerformance information should be prepared by management and independently verified, under the oversight of board of directors. Financial information should be subject to an independent, audit overseen by the audit committee. Sustainability information is also increasingly expected to be independently verified, following assurance standards for non-financial information.
learn more