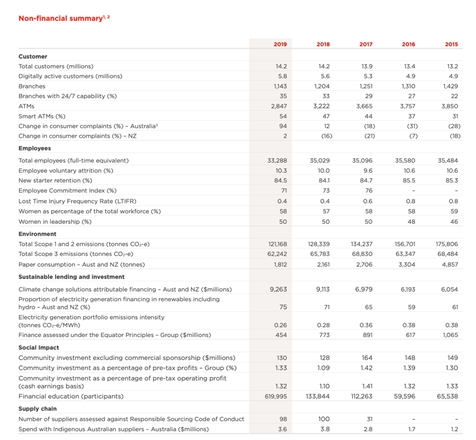
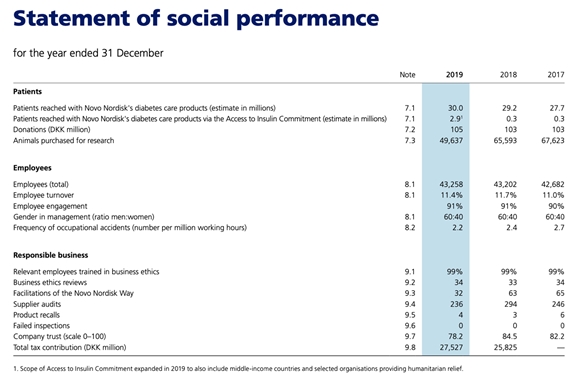
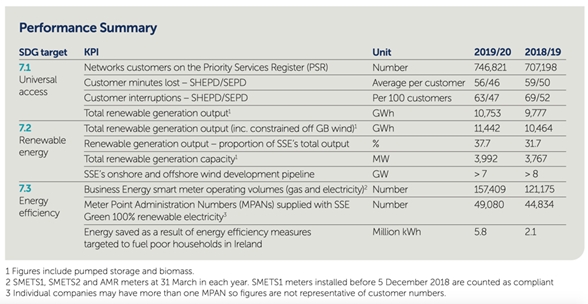
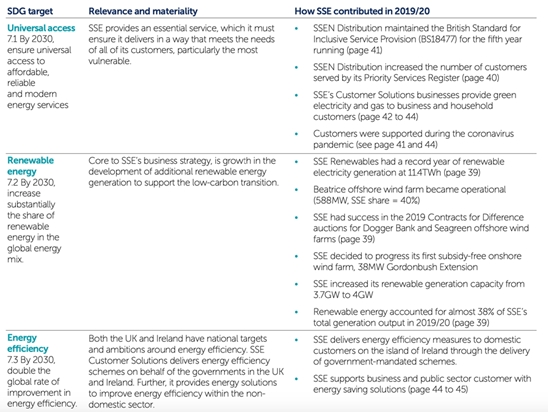
Suggested Metrics For Sustainability Statements
Sustainability statements should include metrics that characterize performance on material issues, including:
- Generic sustainability issues applicable to most industries, and
- Specific issues based on industry, business model, or physical location.
Quantitative information on on sustainability performance can also help investors measure the financial impact of sustainability (extra-financial analysis).
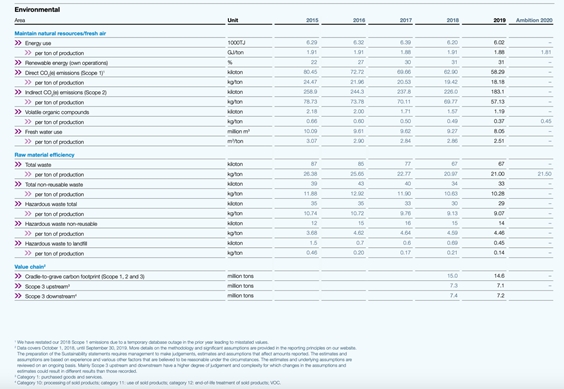
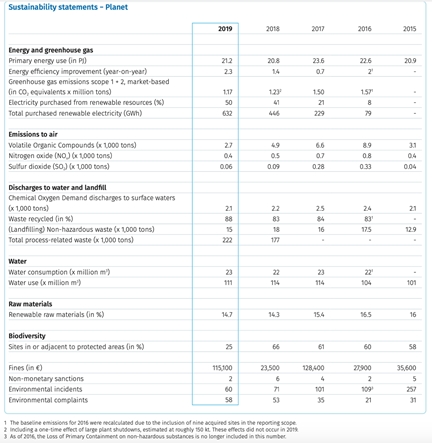
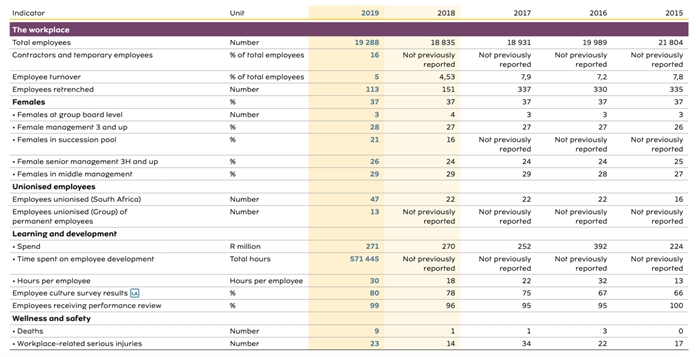
Examples of sustainability metrics
Consult this resource for examples of metrics for Sustainability KPIs and Statements, including:
- Most common ESG Metrics [here]
- Emerging market-focused E&S metrics [here]
- Industry-specific ESG metrics [here]
ESG and extra-financial analysis
Extra-financial analysis consist in identifying and tracking performance on sustainability issues that have a material impacts the operational and financial performance of the company.
initiatives for convergence of ESG Metrics
Consult this resource for a list of recent initiatives aiming at convergence of ESG reporting standards and standardization of sustainability metrics.